How to operate a drone? It’s more than just pushing buttons; it’s about understanding the technology, mastering the controls, and respecting the safety regulations. This guide takes you step-by-step through the process, from pre-flight checks to capturing stunning aerial footage, ensuring you’re equipped to fly responsibly and confidently. We’ll cover everything from basic maneuvers to advanced flight planning, offering practical tips and troubleshooting advice along the way.
Whether you’re a beginner eager to explore the world from a new perspective or an experienced pilot looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive guide will enhance your drone piloting journey. We’ll delve into the intricacies of drone operation, focusing on safe practices, effective techniques, and legal considerations to ensure a rewarding and risk-mitigated experience.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight inspection is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient drone operation. This involves checking various components and verifying environmental conditions to mitigate potential risks. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, equipment damage, and even injury.
Pre-Flight Inspection Steps
A systematic pre-flight inspection is essential. The following steps, organized for clarity, should be followed before every flight:
| Step | Check Item | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Battery Level | Verify the battery is sufficiently charged and in good condition. | Check voltage and ensure no visible damage. Replace if necessary. |
| 2 | Propeller Condition | Inspect propellers for cracks, chips, or other damage. | Replace any damaged propellers. |
| 3 | GPS Signal Strength | Ensure a strong GPS signal is acquired before takeoff. | Wait for a stable signal; consider relocating if signal is weak. |
| 4 | Gimbal Function | Test the gimbal’s movement to ensure smooth operation. | Check for any unusual noises or resistance. |
| 5 | Camera Functionality | Confirm the camera is functioning correctly and recording properly. | Take a test photo or video. |
| 6 | Flight Controller Status | Verify that the flight controller is functioning correctly. | Check for any error messages. |
| 7 | Radio Control Connection | Ensure a stable connection between the remote controller and the drone. | Check for signal strength and any interference. |
| 8 | Environmental Conditions | Assess wind speed, precipitation, and visibility. | Postpone flight if conditions are unsafe. |
Safety Briefing and Hazard Mitigation
Understanding potential hazards and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies is paramount for safe drone operation. Potential hazards include loss of signal, battery failure, collisions with obstacles, and inclement weather. Risk mitigation involves thorough pre-flight checks, maintaining a safe distance from obstacles, and adhering to flight regulations.
A flowchart visualizing the pre-flight procedure would enhance understanding and aid in consistent adherence to safety protocols. The flowchart would visually represent the sequential steps, starting from battery checks, progressing through GPS signal verification, and culminating in a final safety check before commencing flight.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Mastering drone controls is essential for safe and effective operation. Understanding the basic controls and flight modes allows for precise maneuvering and avoids potential accidents.
Basic Drone Controls
- Throttle: Controls the altitude of the drone. Increasing throttle raises the drone, decreasing throttle lowers it.
- Yaw: Rotates the drone left or right around its vertical axis.
- Pitch: Tilts the drone forward or backward, controlling its movement in the direction it’s facing.
- Roll: Tilts the drone left or right, controlling its lateral movement.
Flight Modes and Their Functionalities
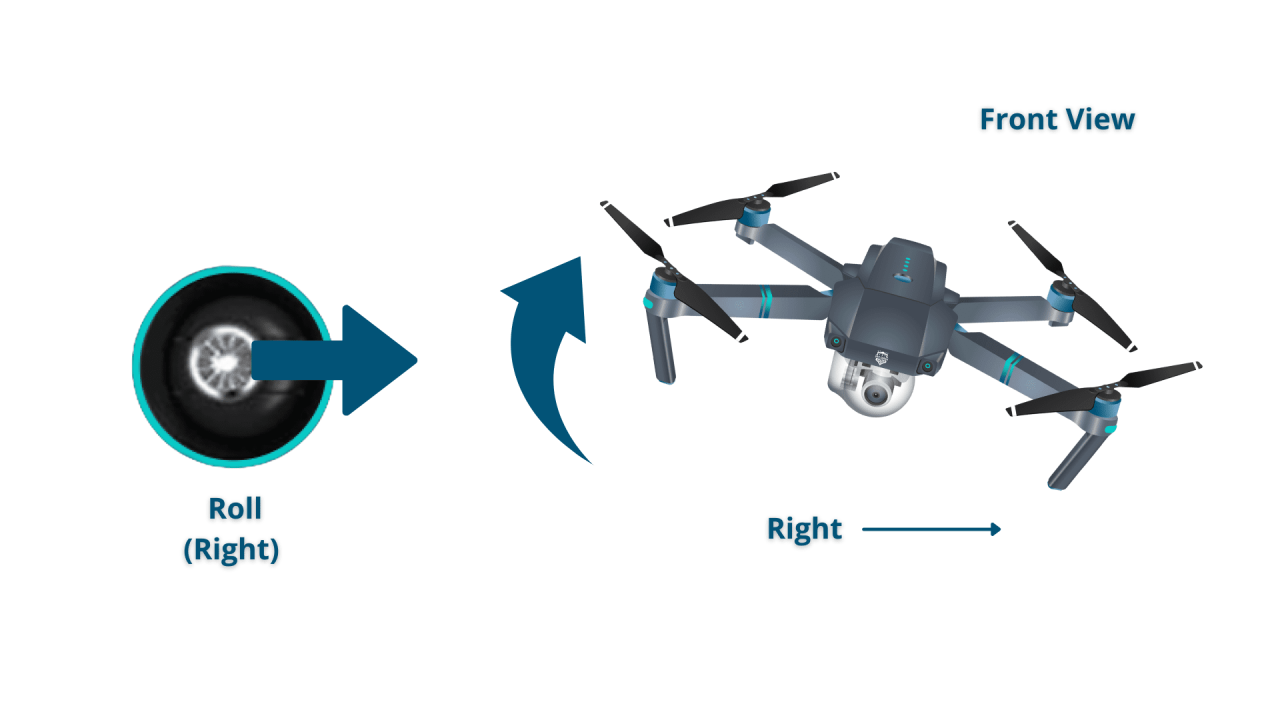
Different flight modes offer varying levels of autonomy and control. GPS mode utilizes satellite data for precise positioning, while Attitude mode relies on onboard sensors for stability, irrespective of GPS signal. Understanding the nuances of each mode is crucial for adapting to different flight conditions and scenarios. For instance, GPS mode is ideal for stable hovering and precise movements, whereas Attitude mode provides more responsive control in environments with weak or absent GPS signals.
Drone Maneuvering Tips and Techniques
Smooth and precise drone maneuvering requires practice and a delicate touch. Avoid abrupt movements, especially in windy conditions. Practice flying in open spaces to build confidence and develop control skills. Using the drone’s return-to-home function can also be a safety feature in case of signal loss.
Compass and Sensor Calibration
Regular calibration of the drone’s compass and sensors ensures accurate readings and stable flight. The calibration process typically involves a series of specific movements, as instructed by the drone’s manufacturer. This process aligns the internal sensors with the external environment, leading to more accurate flight data and improved stability.
Taking Off, Landing, and Emergency Procedures
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are crucial for preventing accidents and damage. Knowing how to handle emergencies can save your drone and prevent injuries.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedures
- Perform a pre-flight check.
- Select an open and level area free of obstacles.
- Slowly increase throttle to lift off vertically.
- Maintain a steady altitude and orientation.
- For landing, gradually decrease throttle and gently lower the drone to the ground.
- Power off the drone after landing.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Solutions
Understanding common drone malfunctions and their solutions is essential for safe operation. Issues such as motor failures, GPS signal loss, and low battery can be addressed through troubleshooting and preventative maintenance. For example, a failing motor might be indicated by unusual sounds or vibrations, prompting a prompt landing and inspection. GPS signal loss requires a return to an area with better signal reception, while low battery necessitates an immediate landing.
Emergency Scenarios and Procedures, How to operate a drone
Potential emergency scenarios, such as low battery, loss of signal, or unexpected malfunctions, require swift and decisive action. Having a pre-planned emergency procedure can significantly reduce the risk of damage or injury. In the event of low battery, for instance, the drone should be landed immediately in a safe location. Loss of signal might necessitate activating the return-to-home function, assuming it’s available and functioning properly.
Emergency Landing Checklist
A checklist outlining actions to take during an emergency landing ensures a systematic response. This checklist would cover aspects such as assessing the situation, identifying the nearest safe landing zone, executing a controlled descent, and securing the drone post-landing. This helps maintain composure and prioritize safety in a stressful situation.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering flight controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of safety regulations and best practices. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic controls to advanced maneuvers, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and ensure you’re prepared for a safe and enjoyable flight experience.
Remember, responsible drone operation is crucial for everyone’s safety.
Flight Planning and Route Optimization: How To Operate A Drone
Flight planning, particularly for longer flights or complex maneuvers, is crucial for efficiency and safety. Optimizing the flight path helps to avoid obstacles, conserve battery life, and achieve the desired results.
Importance of Flight Planning
Flight planning allows for a proactive approach to flight operations, mitigating potential risks and enhancing overall efficiency. This involves mapping out the flight path, considering factors like wind direction, obstacles, and airspace restrictions. A well-planned flight reduces the likelihood of collisions and ensures the drone completes its mission successfully.
Examples of Flight Paths
A simple flight path might involve a straight line from point A to point B, suitable for straightforward aerial photography. A more complex path could involve a series of waypoints, allowing for capturing multiple perspectives and covering a wider area. Visualizing these paths as lines on a map aids in planning and execution. For instance, a path around a building would involve multiple waypoints to capture all sides, while a path over a field might be a simple straight line.
Strategies for Optimizing Drone Battery Life
Maximizing drone battery life involves careful planning and efficient flight techniques. Avoiding rapid ascents and descents, minimizing sudden changes in direction, and maintaining a steady flight speed can all help extend flight time. Flying in calm conditions and utilizing features like return-to-home can also contribute to battery conservation.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is a comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers pre-flight checks and maneuvering techniques. Mastering these skills ensures safe and efficient drone operation, ultimately leading to a positive flying experience.
Sample Flight Plan

A sample flight plan might involve a series of coordinates and altitudes, clearly outlining the drone’s trajectory. This information is essential for precise navigation and achieving the desired shots. For example, a plan might include starting coordinates (latitude and longitude), an altitude of 50 meters, then waypoints at specific intervals, and finally, ending coordinates and a safe landing zone.
| Waypoint | Latitude | Longitude | Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 34.0522° N | 118.2437° W | 50 |
| 2 | 34.0525° N | 118.2440° W | 50 |
| 3 | 34.0528° N | 118.2443° W | 50 |
Drone Photography and Videography Basics
Understanding basic camera settings and techniques is crucial for capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos.
Drone Camera Settings
Key camera settings include resolution (e.g., 4K, 1080p), frame rate (e.g., 24fps, 30fps, 60fps), and exposure (aperture, shutter speed, ISO). Adjusting these settings based on lighting conditions and desired effects is important for achieving optimal image quality. Higher resolutions capture more detail but require more storage space, while higher frame rates create smoother videos but also increase file sizes.
Achieving Different Camera Angles and Perspectives
Experimenting with different camera angles and perspectives allows for creative storytelling and capturing unique viewpoints. Tilting the camera, changing altitude, and maneuvering the drone strategically can create dynamic and visually appealing shots. A low-angle shot can emphasize scale, while a high-angle shot provides a broader overview of the scene. Side-angle shots can highlight details and textures, while aerial perspectives offer unique vantage points.
Tips and Techniques for High-Quality Capture
Techniques for capturing high-quality photos and videos include using a stable platform, understanding lighting conditions, and employing proper composition rules. Maintaining a steady hand and minimizing camera shake are crucial for sharp images and smooth footage. Proper lighting ensures optimal exposure and avoids overexposed or underexposed areas. Following basic composition rules, such as the rule of thirds, can create more visually engaging content.
Composing a Compelling Shot
Composing a compelling shot involves considering the subject, background, and overall composition. Using leading lines, framing techniques, and depth of field can create more visually interesting and impactful imagery. For instance, a leading line could be a road or river leading the viewer’s eye towards the main subject. Framing could involve using natural elements like trees or buildings to create a border around the subject.
Depth of field, controlled by aperture, can blur the background and emphasize the subject.
Drone Maintenance and Storage
Regular maintenance and proper storage are essential for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its optimal performance.
Regular Maintenance Tasks

Regular maintenance includes inspecting propellers, cleaning the camera lens, checking battery health, and lubricating moving parts. This helps identify potential issues early on and prevents more significant problems down the line. For instance, inspecting propellers for cracks or damage is vital for safe flight. Cleaning the camera lens ensures clear images, while checking battery health ensures sufficient power for each flight.
Cleaning and Storage Procedures
Proper cleaning involves using soft cloths and appropriate cleaning solutions to remove dirt and debris. Storing the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures protects it from damage and extends its lifespan. Keeping the drone in a protective case also helps prevent accidental damage.
Common Wear and Tear Issues and Solutions
Common wear and tear issues include propeller damage, battery degradation, and gimbal wear. Solutions involve replacing damaged propellers, properly managing battery usage, and ensuring proper gimbal care. Regular inspections and proactive maintenance can prevent these issues from becoming major problems.
Maintenance Schedule
| Task | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Inspect propellers | Before each flight | Check for cracks, chips, or damage. |
| Clean camera lens | After each flight | Use a soft cloth and lens cleaning solution. |
| Check battery health | Weekly | Monitor voltage and charging cycles. |
| Inspect gimbal | Monthly | Check for smooth movement and any unusual noises. |
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone requires adherence to local, state, and federal regulations. Understanding and complying with these regulations is crucial to avoid legal penalties and ensure safe operation.
Relevant Regulations and Laws
Regulations vary by location, covering aspects such as registration, licensing, airspace restrictions, and operational limits. It is essential to research and understand the specific rules in your area before operating a drone. These regulations often aim to ensure safe operation and prevent interference with other aircraft or sensitive areas.
Obtaining Necessary Permits and Licenses
Depending on your location and intended use, obtaining permits and licenses might be necessary. These permits often require completing training courses and demonstrating a certain level of competency in drone operation. The specific requirements vary by jurisdiction and the type of drone operation.
Airspace Restrictions and No-Fly Zones
Airspace restrictions and no-fly zones are designated areas where drone operation is prohibited or restricted. These zones are often near airports, government buildings, or other sensitive locations. It is crucial to check for airspace restrictions before each flight to avoid legal issues and ensure safe operation.
Legal Requirements Checklist
A checklist of legal requirements would cover aspects such as registration, licensing, airspace restrictions, and operational limits specific to your area. This checklist helps ensure compliance and reduces the risk of legal penalties.
Mastering drone operation is a rewarding experience that combines technology, skill, and responsibility. By following the guidelines Artikeld in this guide—from meticulous pre-flight checks to post-flight maintenance—you’ll not only enhance your piloting capabilities but also ensure the safety and longevity of your drone. Remember that continuous learning and adherence to regulations are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot.
Embrace the possibilities, fly safely, and enjoy the breathtaking perspectives that await you.
Top FAQs
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and autonomous flight modes are ideal for beginners. Look for models with features like obstacle avoidance and return-to-home functionality.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant magnetic interference.
What should I do if I lose signal with my drone?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If it doesn’t work, try to visually locate your drone and attempt a manual landing.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies depending on the model and flight conditions. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes, often less in demanding conditions.
Where can I find information on local drone regulations?
Check your local civil aviation authority’s website for specific regulations regarding drone operation in your area. The FAA (in the US) and equivalent organizations in other countries provide detailed information.
